Back to: PRIMARY SEVEN P7 SCIENCE TOPICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Electric circuit
Qn. What is an electric circuit?
- An electric circuit is the path followed by electricity.
OR - An electric current is a path taken by electricity.
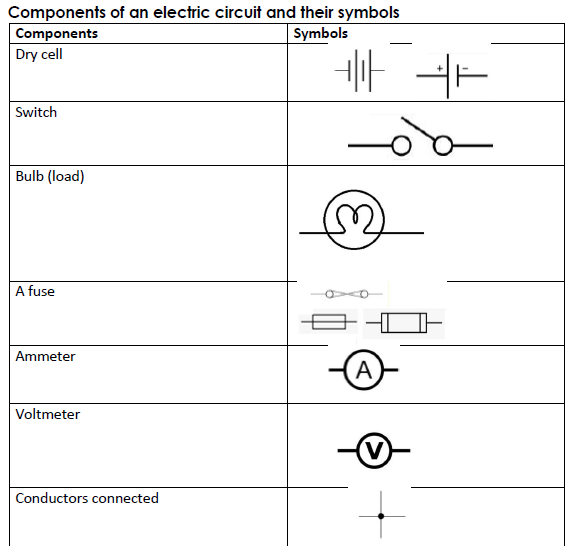
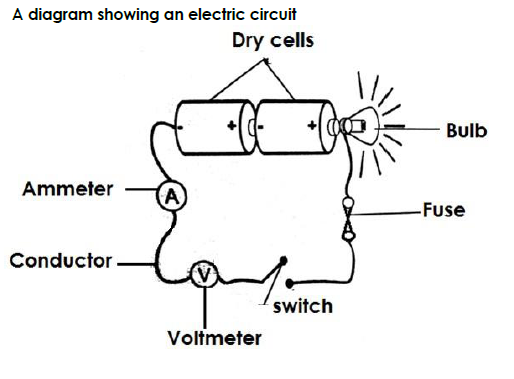
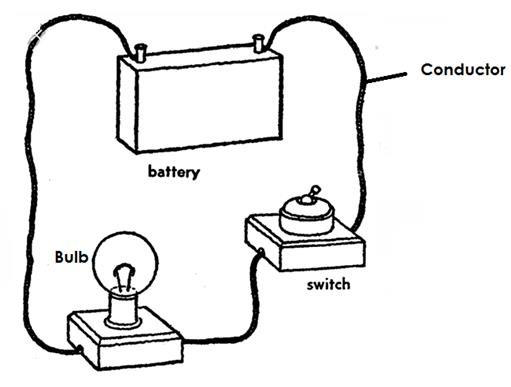
Qn. State the function of each of the parts of an electric circuit.
A) Switch
- The switch breaks and completes the circuit at the user’s will.
b) Ammeter - The ammeter measures electric current.
c) Conductor - The conductor transmits electricity through the circuit.
d) Dry cells - The dry cells produce electricity for the appliance.
Qn. Name the form of energy stored in a dry cell. - Chemical energy
Qn. What energy charge takes place when the circuit is complete? - Chemical energy changes to electric energy.
e) Bulb - The bulb gives light.
Qn. Identify the form of energy stored in an electric bulb, - Electric energy.
Qn. State the energy change that takes place in an electric bulb when the circuit is complete. - Electric energy changes to light energy.
Qn. Identify the two forms of energy produced by an electric bulb when the circuit is complete. - Heat energy
Light energy
State two cases that can make a bulb fail to give out light in a circuit when the switch is pressed. - Poor arrangement of dry cells.
- When the conductor is not connected properly.
- When the bulb is not fixed properly.
Qn. Identify the instances / factors that can make a bulb to stop giving light even when the circuit is complete. - When the dry cells are used up.
- When the filament burns out.
- When the fuse blows.
f) Fuse - A fuse breaks the circuit incase of too much flow of current.
Qn. How does the fuse work? - By melting and breaking the circuit incase of too much flow of current.
Qn. How is a fuse adapted to its function? - A fuse has a low melting point.
Qn. Give the factors that can make a fuse wire to blow. - When the fuse is too old.
- When there is a short circuit.
- Over loading of the circuit
Note: - A fuse is made up of an alloy of tin and lead which has a low melting point.

Leave a comment