Back to: BIOLOGY NEW LOWER SECONDARY CURRICULUM BOOK 2
Comparing the water retention capacity of sandy clay and loam soils Duration: 80 Minutes
Key question: What is the difference in water retention capacity of soils?
What you need
- measuring cylinders (3)
- funnels (3)
- water
- filter papers or piece of cotton
wool soil samples: sandy soil, clay soil and loam soil
What to do
- In groups, using the materials you have been provided with design an experiment to compare the water retention capacity of loam, sandy and clay soils.
- Conduct the experiment you have designed and write a report on your investigation
3. Present your report to the rest of the class using a graph or a table.
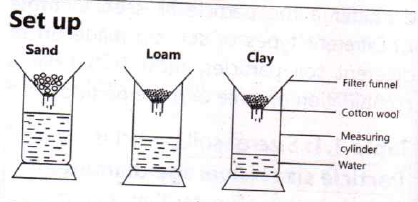
Observation: Water passes through sandy soil faster than it does in loam and clay soils. Sandy soil gives the first drop of water and clay soil gives the last drop. So much water is collected in the cylinder with sandy soil and the least water is collected in the cylinder with clay soil.
Conclusion: Clay soil holds more water than loam and sandy soils.
Explanation: Sandy soil has larger air spaces which enable water to pass through more rapidly and on the other hand, clay soil retains more water than sand and loam soils. This is because clay soil has many small particles with small air spaces thereby retaining more water. Loam soil has medium retention.
b) Water drainage
Help the learners understand that rain water seeps to the bottom layers of soil and in places where this is impossible there: is flooding (Figure 1.4). Ask the learners to share their experience about floods,then guide them to understand that drainage is the ability of a soil water to pass through it and that it varies in different soils.

Figure 1.4: Flooded area due to poor soil drainage

I will immediately snatch your rss as I can not find
your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you have
any? Kindly allow me know so that I may subscribe.
Thanks.
This definition is authentic