Back to: PRIMARY SEVEN P7 SCIENCE TOPICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Domestic electricity The electricity we use in our homes is connected to an electric meter with both the live and neutral wires.
Qn. State the function of the electric meter.
- The electric meter measures electricity used in a house / building.
Qn. In which units is electricity measured? - Kilowatt hours (KWH).
Devices connected to electricity
Qn. Mention the devices connected to electricity. - Generator
- Transformer
- Dynamo
- Electric motor
a) Generator - A generator is a device that produces electricity by changing mechanical energy to electric energy.
Qn. How is a generator able to produce electricity? - By rotating coils of wires in a magnetic field.
Qn. Identify the types of generators. - Alternating current generator (A.C Generator)
- Direct Current Generator (D. C. Generator)
Qn. How can a generator be made to produce more electricity? - By increasing the number of turns in a coil.
- By increasing the magnetic field.
- By increasing the speed of rotation.
b) Dynamo
Qn. How does a dynamo produce electricity? - By changing mechanical energy to electric energy.
Qn. Give examples of devices that use dynamos. - Bicycle
- Vehicles
An illustration of a dynamo

Qn. How does a dynamo work?
- A dynamo works by changing mechanical energy in form of kinetic energy to electric energy.
Qn. State how electric current of a dynamo can be increased. - By increasing the speed of pedaling. Qn. State the importance of dynamos.
- Dynamos in vehicles are used to charge batteries.
- Dynamos are used to produce electricity for lighting.
c) Transformer - A transformer is a device that steps up or steps down voltage of electricity produced.
Qn. Identify the types of transformers. - Step up transformers.
- Step down transformers.
d) Electric motor - An electric motor is a device that changes electric energy to mechanical energy.
Qn. State the uses of electric motors - Electric motors are used to start car engines.
- Electric motors are used in radios.
- Electric motors are used in sewing machines.
- Electric motors are used in fans.
Electricity transmission in Uganda
Qn. Name the organization that supervises electricity in Uganda. - Electricity Regulator Authority (ERA).
Note: - E.R.A replaced Uganda Electricity Board (U.E.B)
Qn. Mention the three companies of E.R.A - Uganda Electricity Generation Company Limited (UEGCL)
- Uganda Electricity Transmission Company Limited (UETCL)
- Uganda Electricity Distribution Company Limited (UEDCL)
Qn. State the role of UEGCL - To generate electricity from power station.
Qn. State the roles of UETCL - To transmit electricity from the power station to different parts of Uganda.
- To buy electricity from generation companies to distribution companies.
- UETCL constructs and maintains sub-stations in Uganda.
- UETCL is responsible for importing and exporting electricity in Uganda.
Qn. State the roles of UEDCL (UMEME) - UMEME connects and distributes electricity to customers from pole
(grid). - UMEME disconnects electricity from electricity defaulters.
Qn. Identify the problems faced by UMEME. - Corruption by UMEME workers.
- Illegal connection by customers.
- Bush burning that may lead to destruction of poles.
- Delayed payments by customers.
- Stealing of electric poles and wires.
- Siphoning of oil from transformers.
Qn. State the roles of ERA
ERA gives licences to the companies that may wish to generate electricity. - ERA supervises and monitors the generation transmission and distribution companies.
- ERA controls the quality of electricity in Uganda.
Qn. How does electricity generated from power stations reach the consumer? - Through transmission lines / wires/cables.
Rural Electrification
Qn. What is rural electrification? - Rural electrification is the extending of electricity to rural areas.
Qn. Why is the government carrying out rural electrification? • To control the massive cutting down of trees for wood fuel.
Static electricity
Qn. What is static electricity? - Static electricity is the type of electricity which does not involve the flow of electrons. Note:
- Static electricity involves stationary charges.
Qn. Identify the charges of static electricity. - Positive charges
- Negative charges
Qn. How is static electricity produced? - Static electricity is produced by friction after rubbing two insulators together.
Qn. State the different ways of creating static electricity in daily life. - By rubbing a ball point pen with hair.
- By rubbing a plastic ruler against a cloth or hair.
- By rubbing polythene against cloth / hair.
- By rubbing a plastic comb against hair.
An illustration
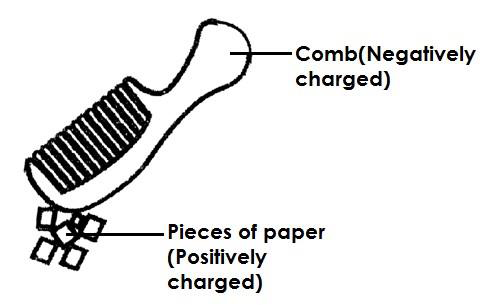
Note:
- Static electricity is produced under the law of electrostatics.
Qn. State the law of electrostatics - Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other.
Qn. State the difference between static electricity and current electricity.
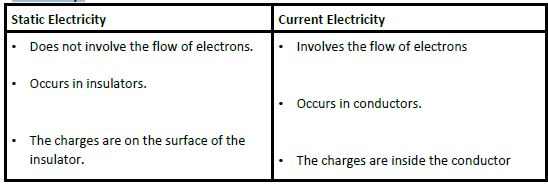

Leave a comment