Back to: PRIMARY SEVEN P7 SCIENCE TOPICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Local action
Qn. What is local action?
- Local action is when hydrogen bubbles are seen coming off from the zinc plate.
Qn. Identify the disadvantages of using wet cells. - Simple cell produce electricity for a short time.
- Simple cells are bulky (not easily carried).
- Simple cells are only used in an upright position.
b) Secondary cells
Qn. What are secondary cells? - Secondary cells are cells that can be recharged once used up.
Note: - Recharging is the process of replacing lost energy in a cell.
Qn. Give the examples of secondary cells. - Car batteries / lead acid batteries / accumulates.
- Phone batteries / mobile phone batteries.
Qn. State the advantages of using secondary cells. - Secondary cells can be recharged.
- Secondary cells have a high voltage.
- Secondary cells can be used in running heavy / strong machines.
Qn. State the disadvantages of using secondary cells. - Secondary cells are expensive.
- Secondary cells are bulky.
- Secondary cells are not easy to maintain.
A car battery
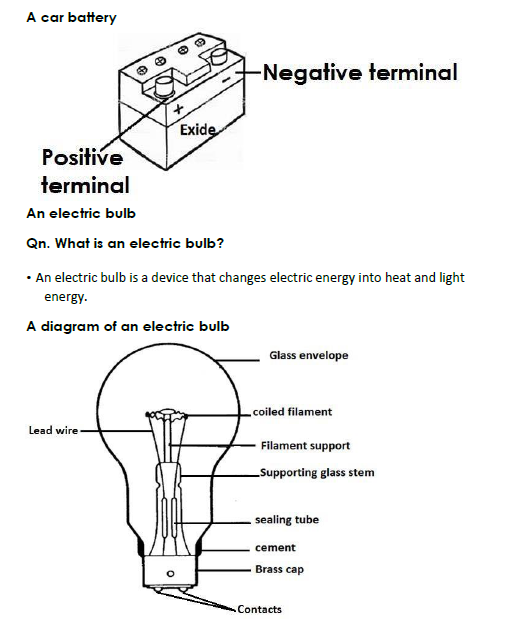
Qn. State the energy change that takes place in a bulb?
- Electric energy is converted to heat and light energy.
Qn. State the function of each part of a bulb.
a) Glass envelope - The glass envelope protects the inside parts of the bulb.
- The glass envelope prevents nitrogen and organ gases from escaping.
Note:
The glass envelope is transparent.
Qn. Why is the glass envelope transparent? - To allow light to pass through.
Qn. Why is argon and nitrogen used in bulbs? - To prevent evaporation of tungsten.
- To prevent oxygen from mixing with the coiled filament.
- To enable the filament burn at a high temperature with out blowing.
Note: - Oxygen cannot be used in an electric bulb because it leads to melting and blowing of the filament.
b) Brass cap - The brass cap enables the bulb to be fixed properly in the lamp holder.
c) Coiled filament - The coiled filament produces light.
Qn. Why is the filament coiled? - To increase electric resistance.
Qn. From which metal is a coiled filament made? • Tungsten
Qn. Why is the coiled filament made of tungsten? - Tungsten has a high melting point.
Qn. Name the mineral from which tungsten is made? - Wolfram
d) Supporting glass stem and filament support. - The supporting glass stem and filament support hold the filament in position.
g) Lead wire - Lead wires conduct electricity from the contact to the filament.
h) Sealing tube - The sealing tube enables air to be removed from the bulb.
i) Contacts - The contacts transmit electricity from the lamp holder to the bulb.
OR - The contacts connect the bulb to the source of electricity from the lamp holder.
j) Cement - The cement provides support to the inside parts of the bulb.

Good work