Back to: PRIMARY SEVEN P7 SCIENCE TOPICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Electric resistance
Qn. What is electric resistance?
- Electric resistance is the opposition to the flow of current in a circuit.
Qn. Which instrument is used to measure electric resistance? - Ohmmeter
Qn. In which units is electric resistance measured? - Ohms
Electric pressure or electromotive force (e.m.f) - Electric pressure is the force that drives current through the resistance of the circuit.
Qn. Name the instrument that measures electric pressure. - Voltmeter
Qn. In which units is electric pressure measured? - Volts
Qn. Why are most electric heaters coiled? - To increase the electric resistance.
Qn. Write e.m.f in full. - Electromotive force.
Conductors and insulators
Conductors and insulators
Qn. What are conductors? - Conductors are materials that allow electricity to pass through them.
Give the different examples of conductors of electricity.
Silver - Aluminium
- Tin
- Lead
- Tungsten
- Copper
- Iron
- Wet wood.
- Salt solution
- Acids e.g. hydrochloric acid
- Undistilled water / water containing mineral salts.
- Carbon rod.
Qn. Name the non-metallic conductor of electricity. - Carbon rod
Qn. Give a reason why distilled water does not conduct electricity. • Distilled water lacks mineral salts
Note: - Silver is the best conductor of electricity.
Qn. Why are most overhead conductors of electricity made of copper and not silver? - Copper is cheaper than silver.
- Copper is readily available while silver is rare.
- Copper is light while silver is heavy.
Qn. State the uses of conductors - Conductors are used to make electric circuits.
Conductors are used to make electric wires.
What are insulators?
Insulators are substances that do not allow electricity to pass through them.
Qn. Give examples of insulators. - Rubber
- Plastics
- Clothes
- Dry wood
- Dry paper
- Porcelain
- Distilled water
Qn. Give reasons why electric wires are covered with rubber during electrical installation. - To prevent short circuits
Qn. State the uses of insulators - Insulators are used to cover electric wires during electrical installation.
- Insulators are used to cover handles of electric irons / flat irons.
Short circuit
Qn. What is a short circuit? - A short circuit is an electric path with low resistance to the flow of current
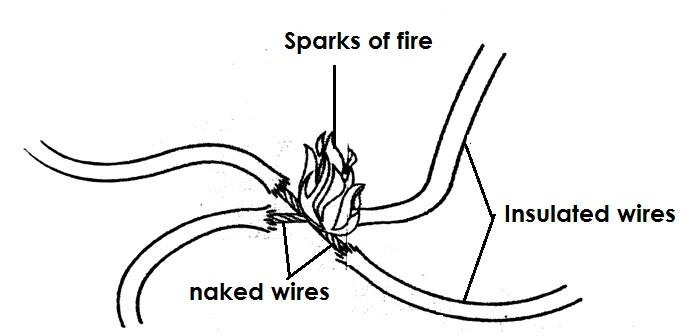
State the main cause of a short circuit.
A short circuit is mainly caused when two naked wires carrying current meet.
Qn. Give the other causes of short circuit.
- Improper connection of electric wire.
- Overloading of circuit.
- Pushing metallic objects into electric circuits.
- Pouring water in electric appliances.
- Damage done by rat to the insulating wires.
- Bad weather conditions that may lead to damage of electric poles.
Qn. State the dangers of short circuits. - Short circuits lead to destruction of electric appliances.
- Short circuits lead to destruction of buildings.
- Short circuits lead to death of people and animals.
Qn. Identity the ways of preventing short circuit. - Electric wires should be well insulated.
- Installation of electricity should be done by experts.
- Repair of electric appliances should be done by experts.
- Old electric wires should be replaced by new ones.
- Avoid overloading of circuits.
- Avoid pushing metallic objects into sockets.
Electric cells
Qn. What is an electric cell? - An electric cell is a device that stores and produces electricity due to a chemical reaction.
Identify the two types of electric cells
Primary cells - Secondary cells
a) Primary cells
Qn. What are primary cells? - Primary cells are cells that cannot be recharged when used up.
Qn. Give the examples of primary cells - Dry cells
- Wet cells / simple cells
- Dry cell
Qn. How does a dry cell produce electricity? - A dry cell produces electricity by changing chemical energy to electric energy.
Note:
A dry cell produces an electromotive force of 1.5 volts

State the function of each part of a dry cell.
a) Brass cap
- A brass cap is the contact to the positive terminal.
b) Pitch / Top seal - The pitch prevents the electrolyte from drying up.
c) Insulating cardboard - The insulating cardboard protects the inside parts of a dry cell. d) Zinc can
- The zinc can act as the negative terminal.
e) Electrolyte (Ammonium chloride paste) • Electrolyte helps in the transfer of electrons.
f) Powdered carbon and manganese dioxide. - Powdered carbon and manganese dioxide act as a depolarizing agent.
OR - Powdered carbon and manganese dioxide prevent bubbles of hydrogen gas from building up around the carbon rod.
g) Carbon rod - The carbon rod acts as a positive terminal.
Note: - The carbon rod is a non-metallic conductor of electricity found in a dry cell.
- The carbon rod is made from graphite.
Qn. What is depolarization? - Depolarization is when hydrogen gas bubbles are prevented from building up around the carbon rod.
Qn. State the advantages of using dry cells. - Dry cells are portable (easy to carry).
- Dry cells are affordable (cheap to buy)
- Dry cells can be used in any position.
Give the disadvantages of using dry cells. - Dry cells cannot be recharged.
- Dry cells produce electricity for a short time.
- Dry cells produce less current that cannot run big machines.
- Used up dry cells can spoil devices.
Simple cells / wet cells
Qn. What is a simple cell? - A simple cell is a cell that consists of a copper plate (positive) and zinc plate (negative) dipped into dilute sulphuric acid.
Note: - Dilute sulphuric acid acts as the electrolyte.
- The zinc plate and copper plate act as electrodes

Leave a comment